Other Relevant Articles
Review Article2017 Jun 6;69(22):2759-2768.
JOURNAL:J Am Coll Cardiol. Article Link
Pothineni NVK, Karathanasis SK, Mehta JL et al. Keywords: LOX-1 blockers; coronary artery disease; endothelial cells; low-density lipoprotein; myocardial infarction; reactive oxygen species
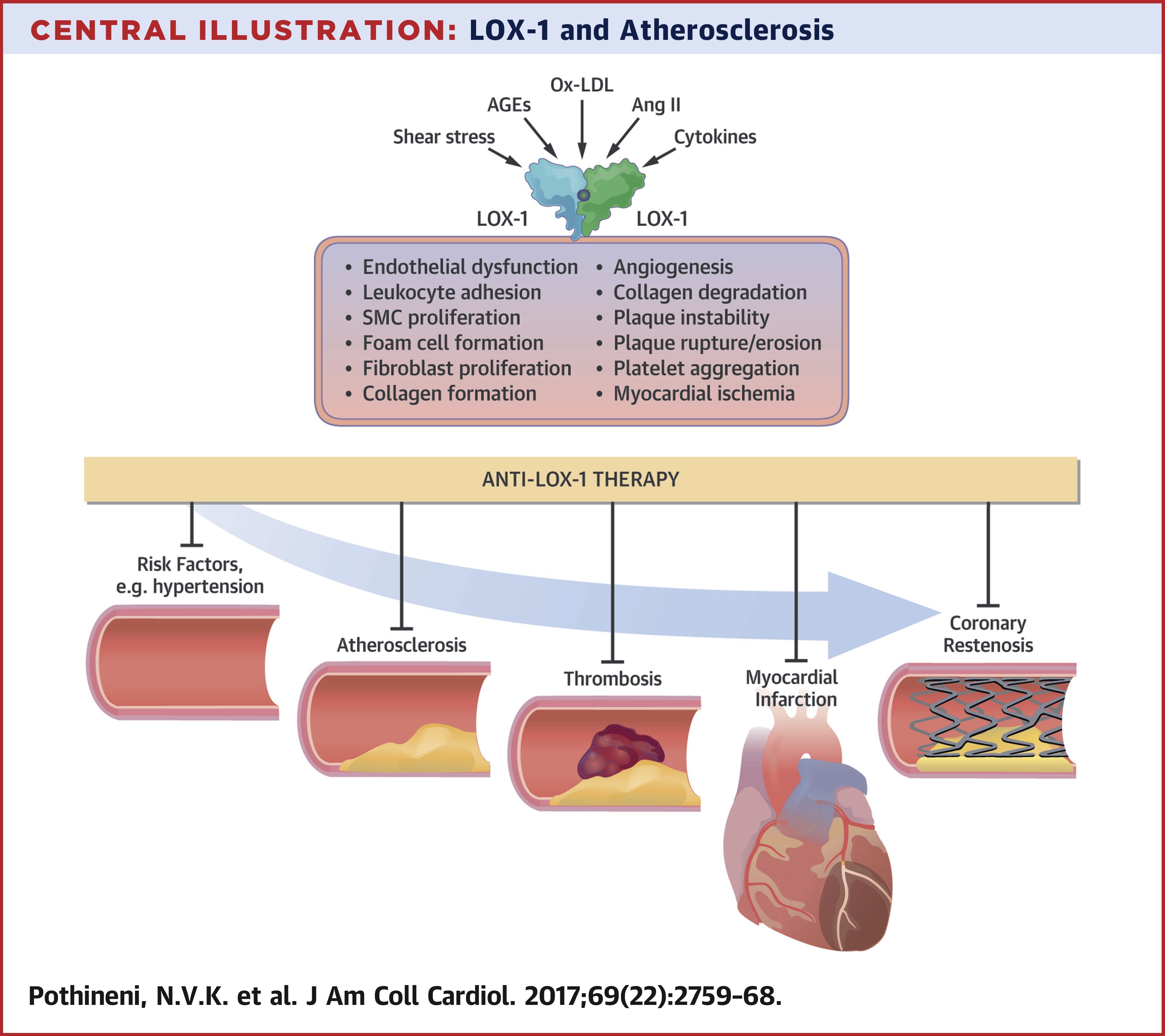
Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1), one of the scavenger receptors for oxidized low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (ox-LDL), plays a crucial role in the uptake of ox-LDL by cells in the arterial wall. Mounting evidence suggests a role for LOX-1 in various steps of the atherosclerotic process, from initiation to plaque destabilization. Studies of the genetic structure of LOX-1 have also uncovered various genetic polymorphisms that could modulate the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular events. As evidence supporting the vital role of LOX-1 in atherogenesis keeps accumulating, there is growing interest in LOX-1 as a potential therapeutic target. This review discusses the discovery and genetics of LOX-1; describes existing evidence supporting the role of LOX-1 in atherogenesis and its major complication, myocardial ischemia; and summarizes LOX-1 modulation by some naturally occurring compounds and efforts toward development of small molecules and biologics that could be of therapeutic use.