推荐文献
Review Article2017 Oct 24;70(17):2186-2200.
JOURNAL:J Am Coll Cardiol. Article Link
Lewis GA, Schelbert EB, Miller CA et al. Keywords: diastolic dysfunction; ejection fraction; heart failure; heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; myocardial fibrosis; titin
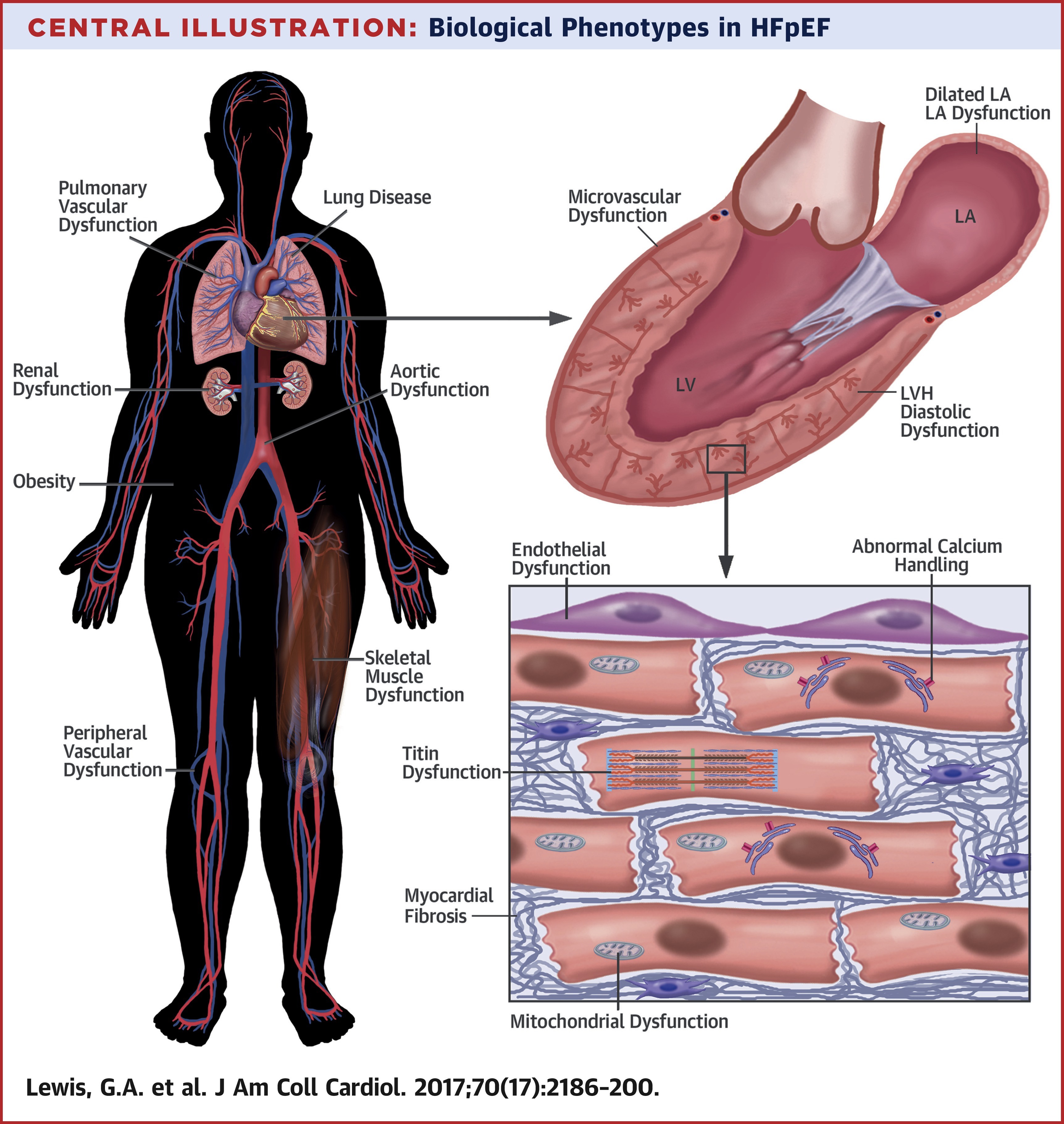
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) involves multiple pathophysiological mechanisms, which result in the heterogeneous phenotypes that are evident clinically, and which have potentially confounded previous HFpEF trials. A greater understanding of the in vivo human processes involved, and in particular, which are the causes and which are the downstream effects, may allow the syndrome of HFpEF to be distilled into distinct diagnoses based on the underlying biology. From this, specific interventions can follow, targeting individuals identified on the basis of their biological phenotype. This review describes the biological phenotypes of HFpEF and therapeutic interventions aimed at targeting these phenotypes.