推荐文献
Clinical Trial2017 Aug 29;70(9):1109-1117.
JOURNAL:J Am Coll Cardiol. Article Link
Yannopoulos D, Bartos JA, Raveendran G et al. Keywords: drug-eluting stent; dual antiplatelet therapy; optical coherence tomography
BACKGROUND - The prevalence of coronary artery disease (CAD) among patients with refractory out-of-hospital(OH) ventricular fibrillation (VF)/ventricular tachycardia (VT) cardiac arrest is unknown.
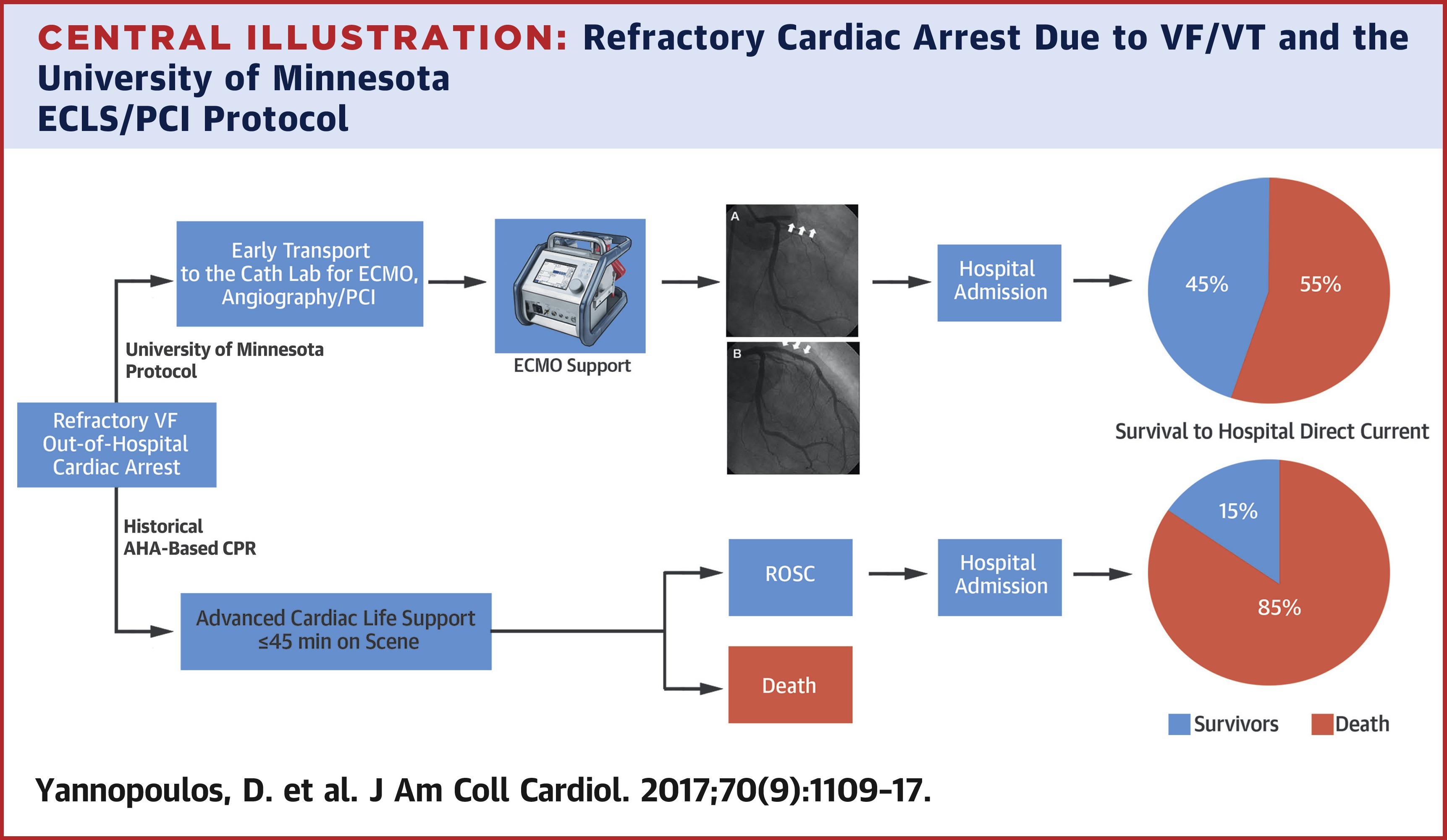
OBJECTIVES - The goal of this study was to describe the prevalence and complexity of CAD and report survival to hospital discharge in patients experiencing refractory VF/VT cardiac arrest treated with a novel protocol of early transport to a cardiac catheterization laboratory (CCL) for extracorporeal life support (ECLS) and revascularization.
METHODS - Between December 1, 2015, and December 1, 2016, consecutive adult patients with refractory OH VF/VT cardiac arrest requiring ongoing cardiopulmonary resuscitation were transported by emergency medical services to the CCL. ECLS, coronary angiography, and percutaneous coronary intervention were performed, as appropriate. Functionally favorable survival to hospital discharge (Cerebral Performance Category 1 or 2) was determined. Outcomes in a historical comparison group were also evaluated.
RESULTS - Sixty-two (86%) of 72 transported patients met emergency medical services transport criteria. Fifty-five (89%) of the 62 patients met criteria for continuing resuscitation on CCL arrival; 5 had return of spontaneous circulation, 50 received ECLS, and all 55 received coronary angiography. Forty-six (84%) of 55 patients had significant CAD, 35 (64%) of 55 had acute thrombotic lesions, and 46 (84%) of 55 had percutaneous coronaryintervention with 2.7 ± 2.0 stents deployed per patient. The mean SYNTAX score was 29.4 ± 13.9. Twenty-six (42%) of 62 patients were discharged alive with Cerebral Performance Category 1 or 2 versus 26 (15.3%) of 170 in the historical comparison group (odds ratio: 4.0; 95% confidence interval: 2.08 to 7.7; p < 0.0001).
CONCLUSIONS - Complex but treatable CAD was prevalent in patients with refractory OH VF/VT cardiac arrestwho also met criteria for continuing resuscitation in the CCL. A systems approach using ECLS and reperfusion seemed to improve functionally favorable survival.
Copyright © 2017 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.