推荐文献
Review Article2017 Jun 13;69(23):2845-2861.
JOURNAL:J Am Coll Cardiol. Article Link
Pinney SP, Anyanwu AC, Lala A et al. Keywords: cardiothoracic surgery; heart failure; hemocompatibility
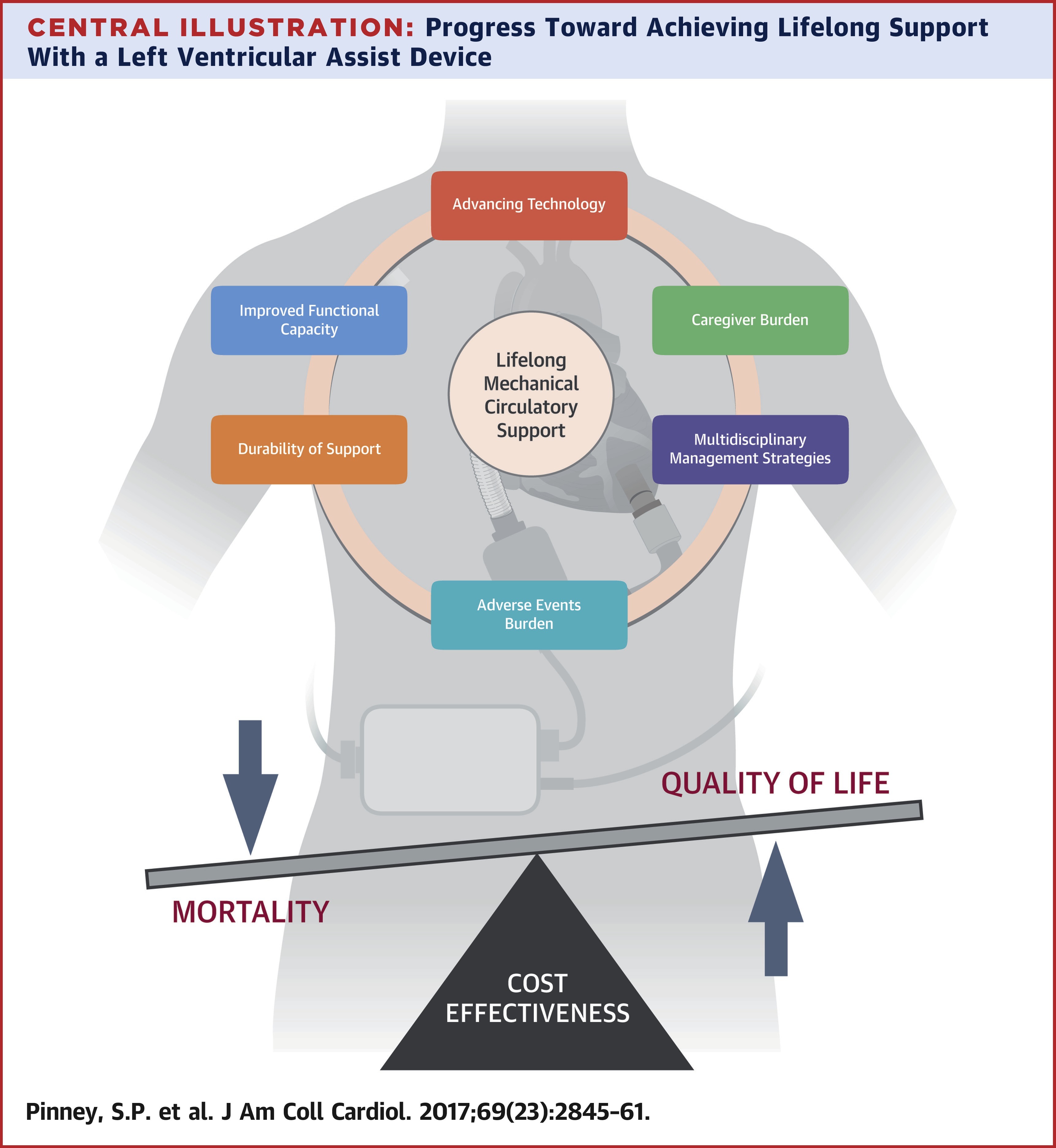
Continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) have revolutionized advanced heart failure care. These compact, fully implantable heart pumps are capable of providing meaningful increases in survival, functional capacity, and quality of life. Implantation volumes continue to grow, but several challenges remain to be overcome before LVADs will be considered as the therapy of choice for all patients with advanced heart failure. They must be able to consistently extend survival for the long term (7 to 10 years), rather than the midterm (3 to 5 years) more typical of contemporary devices; they must incorporate design elements that reduce shear stress and avoid stasis to reduce the frequent adverse events of bleeding, stroke, and pump thrombosis; and they must become more cost-effective. The advancements in engineering, implantation technique, and medical management detailed in this review will highlight the progress made toward achieving lifelong LVAD support and the challenges that remain.