推荐文献
Review Article2017 Jul 11;70(2):230-251.
JOURNAL:J Am Coll Cardiol. Article Link
Niemann B, Newby DE, Kovacic JC et al. Keywords: air pollution; atherosclerosis; diabetes; exhaust; inflammation; metabolic stress; obesity; particulate matter; tobacco
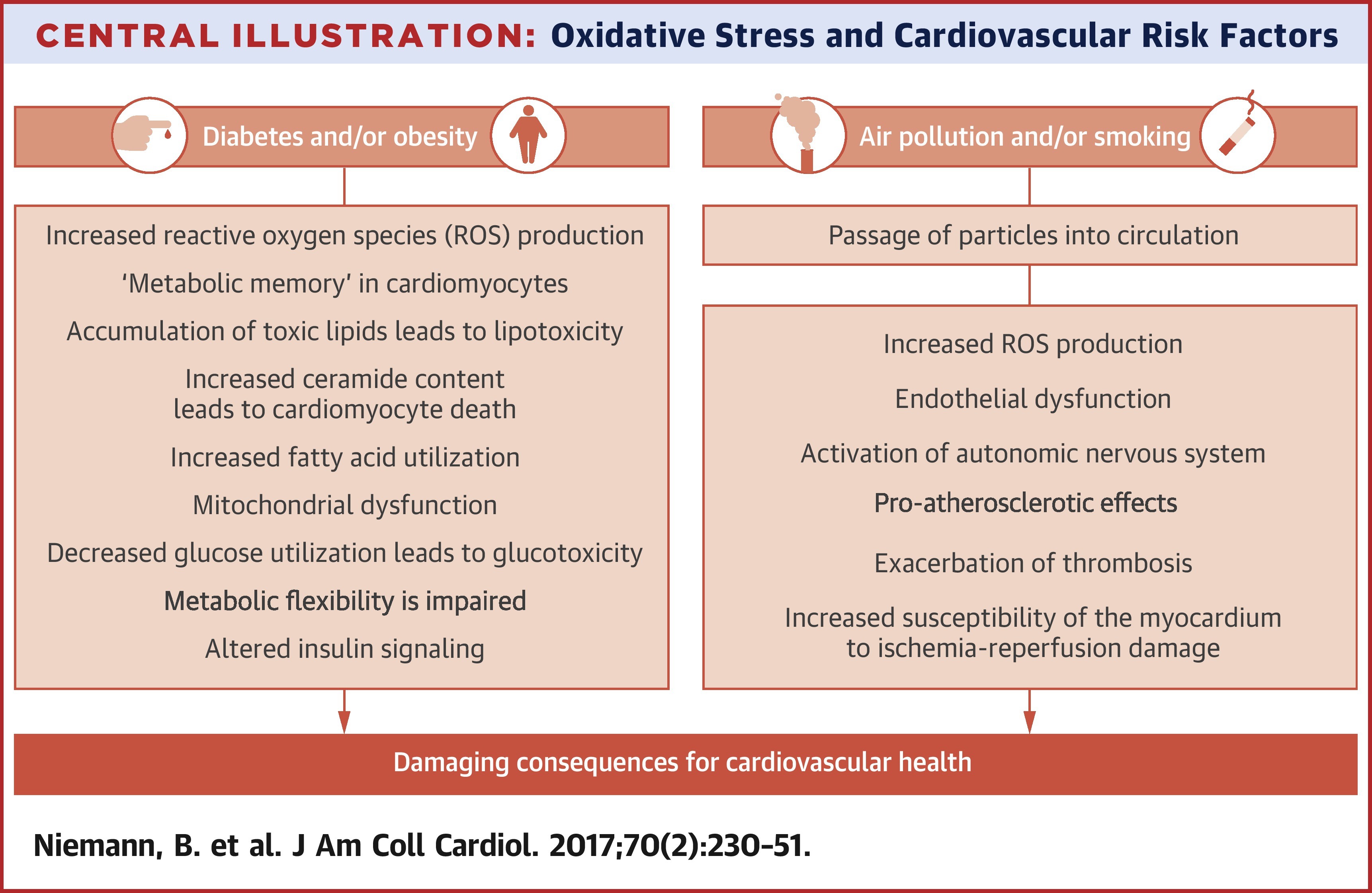
Oxidative stress occurs whenever the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) exceeds endogenous antioxidant capacity. In this paper, we review the specific role of several cardiovascular risk factors in promoting oxidative stress: diabetes, obesity, smoking, and excessive pollution. Specifically, the risk of developing heart failure is higher in patients with diabetes or obesity, even with optimal medical treatment, and the increased release of ROS from cardiac mitochondria and other sources likely contributes to the development of cardiac dysfunction in this setting. Here, we explore the role of different ROS sources arising in obesity and diabetes, and the effect of excessive ROS production on the development of cardiac lipotoxicity. In parallel, contaminants in the air that we breathe pose a significant threat to human health. This paper provides an overview of cigarette smoke and urban air pollution, considering how their composition and biological effects have detrimental effects on cardiovascular health.